Mastering String Multiplication: A Guide to Multiplying String-Represented Integers
By Talent Navigator
Published May 28, 2025
4 min read
Understanding how to multiply string-represented integers is essential for tackling a common coding challenge, especially in interview settings such as LeetCode. This article will detail a step-by-step approach to effectively multiply two numbers represented as strings, all while adhering to the restriction of avoiding direct integer conversion.
The Problem Statement
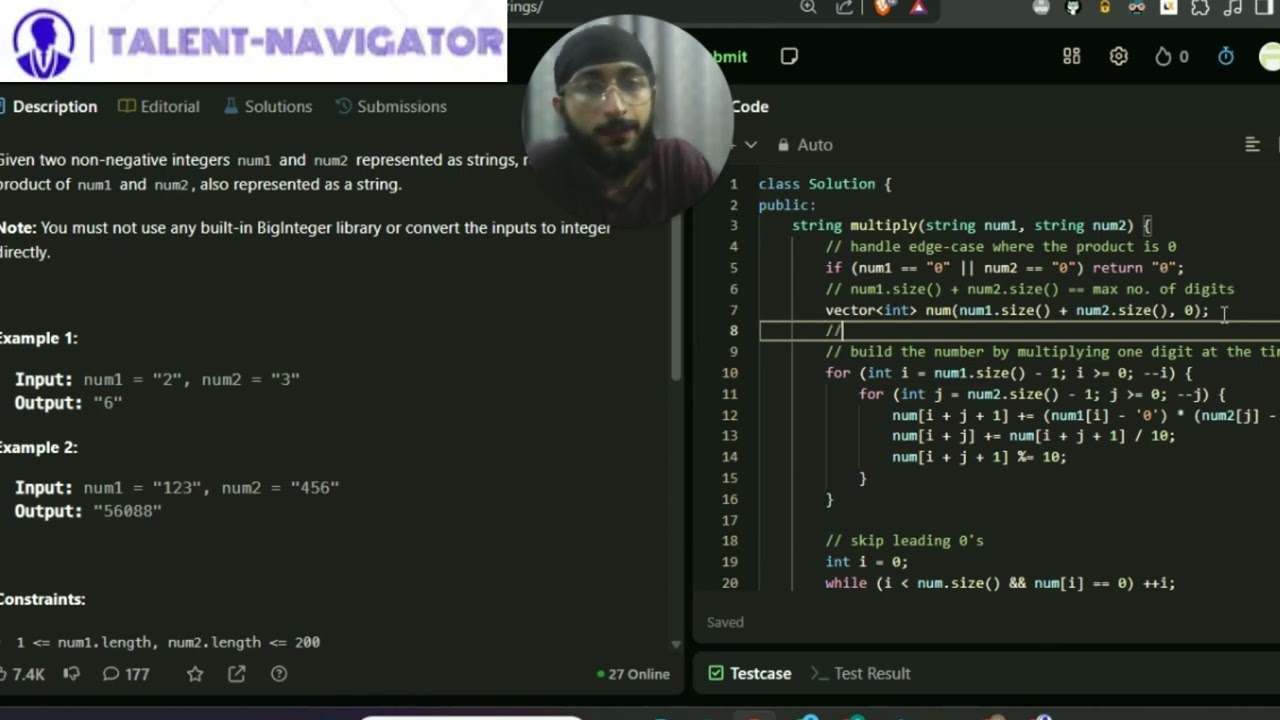
Given two non-negative integers as strings, num1 and num2, the objective is to return their product, also as a string. The challenge lies in the restriction that neither built-in big libraries nor direct conversions to integers can be employed. This forces us to think creatively about how multiplication is fundamentally conducted.
Understanding the Constraints
Before delving into the solution, let’s outline important constraints and considerations:
- Input Types: Inputs will be provided as strings.
- No Direct Conversion: We cannot convert the strings to integers to perform operations directly.
- Output Requirements: The result must also be returned as a string.
Edge Case:
- If either
num1ornum2is "0", the product is "0". Therefore, we can return "0" immediately in this scenario to avoid unnecessary calculations.
Approach to Solve the Problem
To achieve our goal, let’s break down our approach into a structured algorithm:
Step 1: Initialize Variables
- Storage for Result: First, we need storage to hold the result of our multiplication. Since the maximum possible length of the product of two numbers (with m and n as their lengths) can be
m + n, we can create an array (or list) with this length initialized to zero.
Step 2: Multiply Digit by Digit
- Utilize a nested loop where each digit in
num1is multiplied by each digit innum2in a reversed manner (from the least significant digit to the most significant).
Step 3: Compute and Store the Result
- For each digit multiplication, the result will fit into our previously initialized array. If the product of digits is two digits (e.g.,
18when multiplying3and6), we should:- Store the units in the current position (using modulo operation).
- Carry over the tens to the next position in the result array (using integer division).
Step 4: Convert Back to String
- After populating our results array, we need to handle leading zeros and convert the array contents back to a string format.
Step 5: Implementation Details
Python code-
def multiply(num1: str, num2: str) -> str:
if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0":
return "0"
m, n = len(num1), len(num2)
result = [0] * (m + n)
for i in range(m - 1, -1, -1):
for j in range(n - 1, -1, -1):
mul = (ord(num1[i]) - ord('0')) * (ord(num2[j]) - ord('0'))
p1, p2 = i + j, i + j + 1
total = mul + result[p2]
result[p2] = total % 10
result[p1] += total // 10
result_str = ''.join(map(str, result)).lstrip('0')
return result_str if result_str else "0"
Explanation of the Implementation
- Output Handling: After performing all the multiplications and accumulating any carries, we convert the result list back to a string. To prevent leading zeros, we utilize
lstrip('0'). - Character to Integer Conversion: The character-to-integer conversion is achieved by subtracting '0' from the character, thus converting the character to its corresponding integer value.
- Efficiency: This algorithm runs in O(m * n) time, where m is the length of
num1and n is the length ofnum2, making it efficient given the constraints.
Conclusion
Multiplying strings that represent large integers is a common programming challenge that tests one's understanding of fundamental mathematical operations without relying on built-in functionalities. By following this structured approach, programmers can effectively tackle this challenge while gaining deeper insights into string manipulation and number representation in programming.

Comments
Post a Comment